The immune system from the Latin word immunis, meaning: It is made up of different organs, cells and proteins and aside from the nervous system, it is the most complex system that the human body has. And yet, different groups of cells work together and form alliances against just about any pathogen germ. But illness can occur if the performance of the immune system is compromised, if the pathogen is especially aggressive, or sometimes also if the body is confronted with a pathogen it has not come into contact before. Without an immune system, a human being would be just as exposed to the harmful influences of pathogens or other substances from the outside environment as to changes harmful to health happening inside of the body.
Immune System (for Parents)
Usually, the body should not work against its own healthy cells. These are called antigens. The proteins on the surfaces of bacteria , fungi and viruses, for example, are all antigens. When the antigens bind to, for example, special receptors on the defense cells, a series of cell processes is started. The evolutionary older innate immune system provides a general defense against pathogens, so it is also called the nonspecific immune system.
In the adaptive immune system, particular agents like the so-called antibodies target very specific pathogens that the body has already had contact with. That is why this is also called a learned defense or a specific immune response. By constantly adapting and learning the body can also fight against bacteria or viruses that change over time. Yet these two immune systems do not work independently of each other. They complement each other in any reaction to a pathogen or harmful substance, and are closely connected with each other.
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services. Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system.
The suitability of any of the described options in an individual case can be determined by talking to a doctor. For instance, one might make an antibody against the bacteria that cause pneumonia , and another might recognize the common cold virus. Antibodies are part of a large family of chemicals called immunoglobulins, which play many roles in the immune response:. Antibodies lock onto the antigen, but they do not kill it, only mark it for death.
What is the immune system?
The killing is the job of other cells, such as phagocytes. Helper T cells Th cells — they coordinate the immune response.
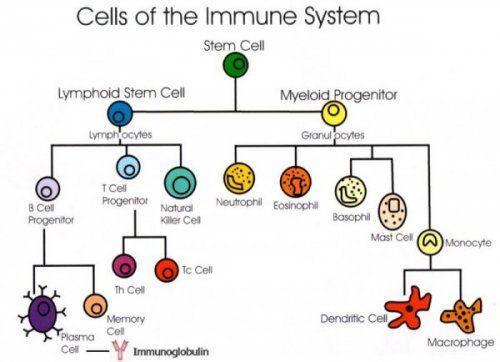
Some communicate with other cells, and some stimulate B cells to produce more antibodies. Others attract more T cells or cell-eating phagocytes. Killer T cells cytotoxic T lymphocytes — as the name suggests, these T cells attack other cells. They are particularly useful for fighting viruses. They work by recognizing small parts of the virus on the outside of infected cells and destroy the infected cells.
Everyone's immune system is different but, as a general rule, it becomes stronger during adulthood as, by this time, we have been exposed to more pathogens and developed more immunity. Once an antibody has been produced, a copy remains in the body so that if the same antigen appears again, it can be dealt with more quickly. That is why with some diseases, such as chickenpox , you only get it once as the body has a chickenpox antibody stored, ready and waiting to destroy it next time it arrives.
This is called immunity.
We are all born with some level of immunity to invaders. Human immune systems, similarly to those of many animals, will attack foreign invaders from day one. This innate immunity includes the external barriers of our body — the first line of defense against pathogens — such as the skin and mucous membranes of the throat and gut. This response is more general and non-specific.
If the pathogen manages to dodge the innate immune system, adaptive or acquired immunity kicks in. This protect from pathogens develops as we go through life. As we are exposed to diseases or get vaccinated, we build up a library of antibodies to different pathogens. This is sometimes referred to as immunological memory because our immune system remembers previous enemies.
This type of immunity is "borrowed" from another source, but it does not last indefinitely. For instance, a baby receives antibodies from the mother through the placenta before birth and in breast milk following birth. This passive immunity protects the baby from some infections during the early years of their life.
- Immune System | Johns Hopkins Medicine Health Library.
- Non-Compliance: The Transition.
- Catherine de Medici: A Biography?
Immunization introduces antigens or weakened pathogens to a person in such a way that the individual does not become sick but still produces antibodies. Because the body saves copies of the antibodies, it is protected if the threat should reappear later in life.
What are lymphocytes?
Because the immune system is so complex, there are many potential ways in which it can go wrong. Types of immune disorder fall into three categories:. These arise when one or more parts of the immune system do not function. Immunodeficiencies can be caused in a number of ways, including age, obesity , and alcoholism. In developing countries, malnutrition is a common cause. AIDS is an example of an acquired immunodeficiency. In some cases, immunodeficiencies can be inherited, for instance, in chronic granulomatous disease where phagocytes do not function properly.
In autoimmune conditions, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells, rather than foreign pathogens or faulty cells. In this scenario, they cannot distinguish self from non-self. Autoimmune diseases include celiac disease , type 1 diabetes , rheumatoid arthritis , and Graves' disease. With hypersensitivity, the immune system overreacts in a way that damages healthy tissue. An example is anaphylactic shock where the body responds to an allergen so strongly that it can be life-threatening.
The immune system is incredibly complicated and utterly vital for our survival. Several different systems and cell types work in perfect synchrony most of the time throughout the body to fight off pathogens and clear up dead cells.
Immune System
Article last updated by Tim Newman on Thu 11 January All references are available in the References tab. How does the immune system work? Understanding the immune system. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Privacy Terms Ad policy Careers.
This page was printed from: Get the most out of Medical News Today. Subscribe to our Newsletter to recieve: Professionally-verified articles Daily or weekly updates Content custom-tailored to your needs Create an account.
More Sign up for our newsletter Discover in-depth, condition specific articles written by our in-house team. Please accept our privacy terms We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your browsing experience, personalize content and offers, show targeted ads, analyze traffic, and better understand you. Sign in Log in with your Medical News Today account to create or edit your custom homepage, catch-up on your opinions notifications and set your newsletter preferences.
Register for a free account Sign up for a free Medical News Today account to customize your medical and health news experiences. Register take the tour. Reviewed by Daniel Murrell, MD. Table of contents White blood cells The immune response Immunity Immune system disorders.
- The immune system: Cells, tissues, function, and disease.
- Love Boat Theme!
- Vidas de Gulliver (Spanish Edition).
- How the immune system works?
- Bobba is My Dad.
- The tasks of the immune system!
- Sexy Model Photography: Hot Panties & Thongs, Underwear Panty and Thong Photos & Pictures of Girls, Babes, Women, & Chicks, Vol. 1!
A white blood cell yellow , attacking anthrax bacteria orange.
![Informed Health Online [Internet].](https://cdn.24.co.za/files/Cms/General/d/2009/2e32c541f462419f8352cf2fc3bd0026.jpg)