When large muscle groups are used, the intensity is moderate to high, and the exercise work is of long duration, weight loss can be expected. Data are given as means and confidence intervals or standard deviation. It should be ascertained that overweight and obese persons do not have any contraindications to additional physical activity.
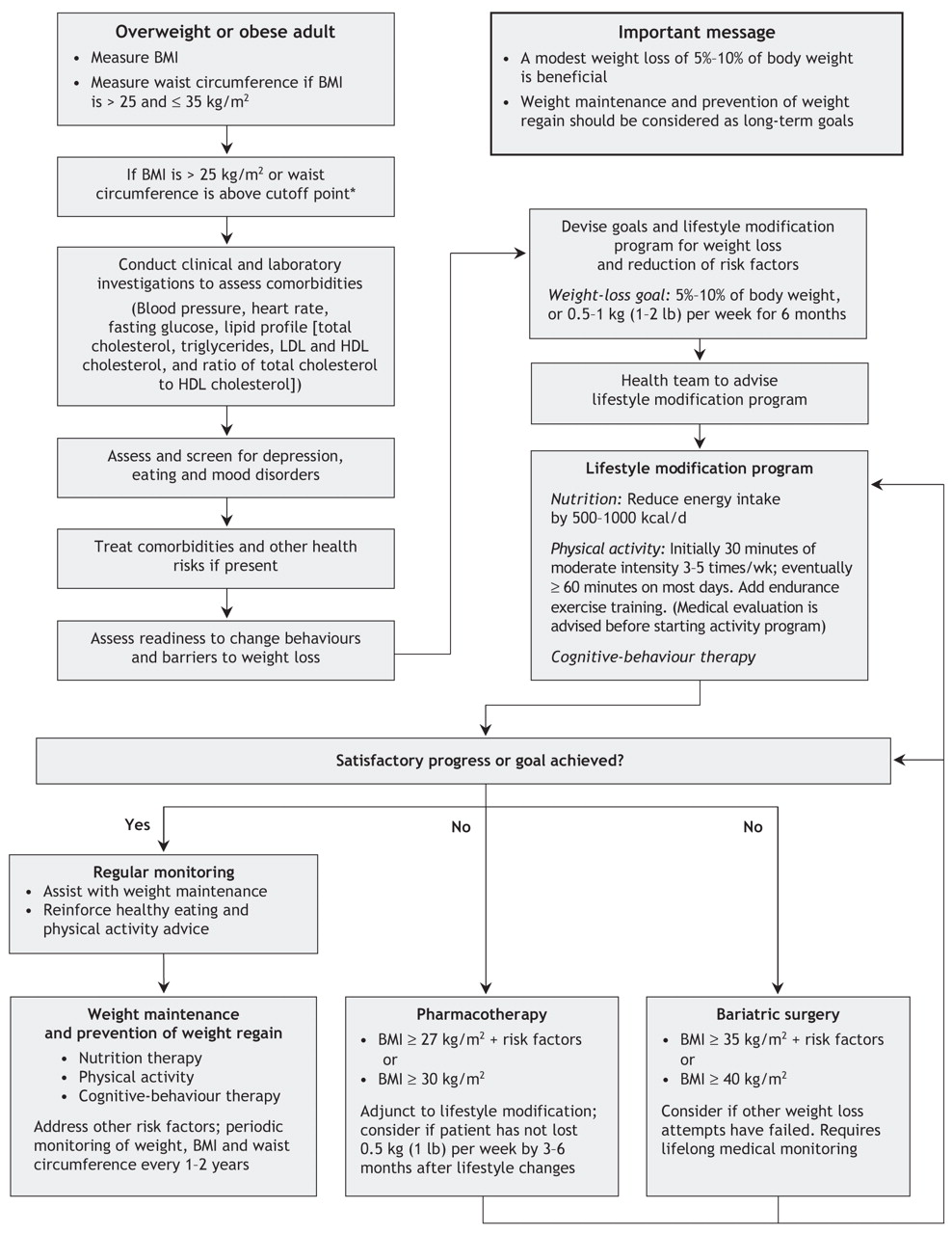
Overweight and obese persons should have the health advantages metabolic, cardiovascular, and psychosocial of physical activity explained to them, which accrue irrespective of loss of weight EL 4, RG A. Even in obese individuals, the health value of increased exercise is seen in more than just a loss of weight Interventions based on a behavioral approach, in a group or individual setting, should form part of a program of weight reduction EL 1, RG A.
The intervention should be aimed primarily at altering lifestyle in terms of nutrition and exercise and may be carried out by qualified non-psychotherapists. If the symptoms accompanying overweight or obesity are more serious e. Various strategies are available for intervention. They should be adapted to the individual situation and the wishes of the patient involved 25 box. Obese patients should be offered weight reduction programs that are adapted to their individual situation and targeted at the therapeutic goals EL 4, RG B.
The weight reduction programs should include the elements of the basic program exercise, diet, and behavioral therapy EL 1—2, RG A.
What Is It?
Table 3 , which gives an overview, includes only programs for which published data are available. The DGEM mentions that obese persons should only be offered programs that have received a positive assessment, which are geared to the individual situation and the therapeutic goals. Programs whose effectiveness is not clear, because for example there are no measured data to show the course of body weight over time, should be excluded.
Drug therapy should only be carried out in combination with a basic program diet, exercise, behavioral therapy. These drugs should be considered as an alternative to antidiabetic drugs that promote weight increase, such as sulfonylureas, glinides, glitazones, and insulin It points out that they may be associated with an increased risk of pancreatic disease.
The drugs have an unacceptable risk—benefit ratio, and in regard to the medical products and dietary supplements, evidence of their effectiveness is lacking. Measures to stabilize body weight long term should take into account aspects of diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy together with the motivation of the patient involved EL 4, RG B.
To support weight stabilization, treatments and consultations should be made available over the long term after successful weight loss, and should include cognitive behavioral therapy EK 1, RG A Patients should be advised, after a period of weight reduction, to maintain an increased level of physical exercise EL 1—2, RG A.
Experience has shown that almost all patients who maintain their weight after a period of weight loss have remained or become physically active After losing 7 to 14 kg, physically active persons regain half their lost weight within 1 to 2 years table 4. Regular weighing contributes to better weight stabilization after successful weight loss EL 4, RG B e2. Compared to conservative treatment, surgical treatment is more effective in terms of body fat reduction, improvement of obesity-related diseases, and reduction of mortality risk e3 — e5 figure 2.
Runkel N, et al.: Dtsch Arztebl Int ; For patients with type 2 diabetes, the recommendation grade is B, as the data are insufficient. Surgical treatment can also be given as a primary therapy, without any preceding conservative treatment, if conservative treatment is judged to have no chance of success or the patient's health does not allow surgery to be delayed in order to attempt improvement by weight reduction EL 4, RG 0. The DGEM regards surgery as indicated in patients who are immobile, in whom diet-based treatment has failed, and in those with a high insulin requirement.
Before surgery, patients should undergo an assessment that includes metabolic, cardiovascular, psychosocial, and dietary details EL 4, RG A. For quality assurance, patients who undergo weight loss surgery should be entered in a central national register EL 4, RG B. Conflict of interest statement. Professor Hauer has received consultancy fees from Weight Watchers International and Apothecom advisory boards. National Center for Biotechnology Information , U. Journal List Dtsch Arztebl Int v. Published online Oct Alfred Wirth , Prof. Author information Article notes Copyright and License information Disclaimer.
Received Jul 17; Accepted Jul See letter " Correspondence letter to the editor: See letter " Correspondence reply: This article has been cited by other articles in PMC. Method Pertinent articles were retrieved by a systematic literature search for the period to Conclusion There is good scientific evidence for effective measures for the prevention and treatment of obesity.
Open in a separate window. Obesity—a disease The World Health Organization WHO , the German Federal Court, the European Parliament, and the German Obesity Association regard obesity as a chronic disease caused by a complex interaction between genetic factors and environmental or lifestyle factors, which carries increased morbidity and mortality and needs lifelong treatment.
Prevention of obesity Given that obesity is so prevalent, and given how difficult it is to treat, prevention is particularly important. Who should lose weight? The following are indicators for treatment: Treatment for obesity Goals Treatment goals should be realistic and adapted to the individual patient e. Dietary therapy Obese individuals should received personalized nutritional recommendations adapted to their therapeutic goals and risk profile EL 4, RG A. To achieve this, various nutrition strategies may be employed EL 1—4, RG 0: Strength training had no measurable effect, not even in combination with endurance training.
There was a positive dose—effect relationship. Interventions for behavior modification Interventions based on a behavioral approach, in a group or individual setting, should form part of a program of weight reduction EL 1, RG A. Box Strategies for weight reduction may have the following psychotherapeutic elements EL 1—2. Practicing flexible, controlled eating and exercise behavior as opposed to rigid behavioral control.
Weight reduction program Obese patients should be offered weight reduction programs that are adapted to their individual situation and targeted at the therapeutic goals EL 4, RG B. Weight-reducing drugs Drug therapy should only be carried out in combination with a basic program diet, exercise, behavioral therapy. Long-term weight stabilization Measures to stabilize body weight long term should take into account aspects of diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy together with the motivation of the patient involved EL 4, RG B.
Table 4 Weight stabilization: Number Characteristics Overall duration Phase 1: Weight reduction kg by reduction diet and exercise Phase 2: Weight loss Phase 2: Surgical intervention in extremely obese patients For extremely obese patients, surgical intervention should be considered EL 1—3, RG A. A low-energy diet is recommended; the ratios between macronutrients fat, carbohydrates, protein is of secondary importance.
But the active ingredient is the same. Other non-prescription diet pills. Over-the-counter diet pills often contain ingredients that can increase heart rate and blood pressure. It is not clear how effective they are in producing weight loss that can be maintained over time. Common side effects include feeling jittery and nervous and having heart palpitations. Some experts believe they may be associated with an increased risk of stroke.
To help you lose weight, your doctor may prescribe medications along with a calorie-restricted diet. Almost all people regain weight when they stop using these medications.
The effects of long-term use of these drugs have not been determined. In general, weight-loss surgery called bariatric surgery may be considered if your BMI is 40 or greater, or your BMI is or greater and you have at least one medical condition directly related to obesity. In addition, you must have participated in a structured weight loss program without success.
The Prevention and Treatment of Obesity
Gastroplasty — also known as stomach stapling. A surgeon creates a small pouch in the stomach that allows only limited amounts of food to be eaten at one time. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. A surgeon places an adjustable band around the stomach with minimally invasive surgery. This is the most effective weight loss surgery. However, it also carries a greater risk of complications, both short term and long term.
A surgeon creates a small pouch in the upper part of the stomach. A hole is made in the small intestine beyond the normal stomach attachment. The pouch is attached to the hole, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the top part of the small intestine.
- .
- In the Line of Fire: How to Handle Tough Questions -- When It Counts.
- Olympus Falling (Legends Collide Book 1).
- Prevention Strategies & Guidelines | Overweight & Obesity | CDC.
Call your doctor if you need help losing weight. Also call if you have any of the symptoms or complications of obesity. Others, however, find it difficult to maintain the weight loss for long. Most people return to their pretreatment weight within five years. Box Bethesda, MD Phone: Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Find out everything you need to know about weight loss drugs in our prescription weight loss pill guide.
By clicking Subscribe, I agree to the Drugs. The easiest way to lookup drug information, identify pills, check interactions and set up your own personal medication records.
Available for Android and iOS devices. Subscribe to receive email notifications whenever new articles are published. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. To view content sources and attributions, please refer to our editorial policy. We comply with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information - verify here. Obesity is an excess of body fat.
The Prevention and Treatment of Obesity
To calculate your BMI: Multiply your weight in pounds by Divide that answer by your height in inches Divide that answer by your height in inches again Then use the chart below to see what category your BMI falls into. BMI Category Below It can also put you at risk of developing a number of conditions. High blood pressure Diabetes Heart disease Some forms of cancer Many other health risks are higher for people who are obese. People become obese for a number of reasons. Screening for Obesity in Pediatric Primary Care: Recommendations from the U.
Preventive Services Task Force Guidance for primary care providers in screening for obesity and offering or referring to comprehensive, intensive behavioral weight management interventions. Skip directly to search Skip directly to A to Z list Skip directly to navigation Skip directly to page options Skip directly to site content. Enter Email Address What's this?
Related Topics Diabetes Nutrition.
