Signs and symptoms Hand, foot, and mouth disease: Who gets and causes Hand, foot, and mouth disease: Diagnosis and treatment Hand, foot, and mouth disease: Tips for preventing Head lice Head lice: Signs and symptoms Head lice: Who gets and causes Head lice: Diagnosis and treatment H ead lice: Tips for managing Herpes simplex Herpes simplex: Signs and symptoms Herpes simplex: Who gets and causes Herpes simplex: Diagnosis and treatment Herpes simplex: Tips for managing Impetigo Impetigo: Signs and symptoms Impetigo: Who gets and causes Impetigo: Diagnosis and treatment Impetigo: Tips for managing Molluscum contagiosum Molluscum contagiosum: Signs and symptoms Molluscum contagiosum: Who gets and causes Molluscum contagiosum: Diagnosis and treatment Molluscum contagiosum: Tips for managing Nail fungus Nail fungus: Scabies burrows may present as papules or pustules in a short linear pattern on the skin, frequently in the web spaces of the fingers.
Onchocerciasis may occur in long-stay travelers living in rural sub-Saharan Africa and, rarely, Latin America. It usually manifests as a generalized pruritic, papular dermatitis.
Common skin diseases and conditions
Bacterial skin infections may occur more frequently after bites and other wounds in the tropics, particularly when good hygiene cannot be maintained. Organisms responsible are commonly Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. Drug-resistant organisms are frequently acquired in the tropics. The presentations can include pyoderma or impetigo, abscess formation, erysipelas, cellulitis, lymphangitis, or ulceration. Furunculosis, or recurrent pyoderma, may be the result of colonization of the skin and nasal mucosa with S. Boils may continue to occur weeks or months after a traveler returns and, if associated with S.
In addition to pyoderma, cellulitis or erysipelas may complicate excoriated insect bites or any trauma to the skin. Cellulitis and erysipelas manifest as areas of skin erythema, edema, and warmth in the absence of an underlying suppurative focus. Unlike cellulitis, erysipelas lesions are raised, there is a clear line of demarcation at the edge of the lesion, and the lesions are more likely to be associated with fever. Cellulitis, on the other hand, is more likely to be associated with lymphangitis.
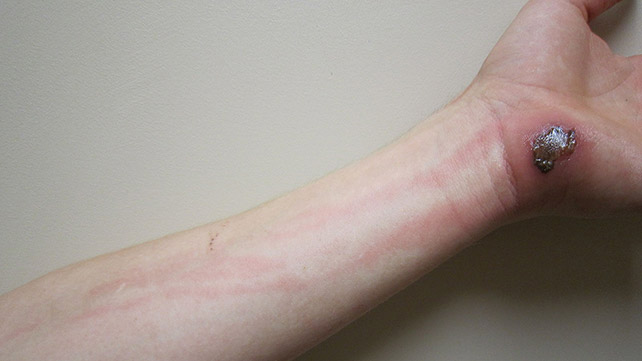
Another common bacterial skin infection, especially in children in the tropics, is impetigo due to S. Local care and a topical antibiotic such as mupirocin may be used, although a systemic antibiotic may be required. Emerging antibiotic resistance among staphylococci and streptococci complicates antimicrobial options. Myiasis presents as a painful lesion similar to a boil. It is caused by infestation with the larval stage of the African tumbu fly Cordylobia anthropophaga or the Latin American bot fly Dermatobia hominis.
At the center of the lesion is a small punctum that allows the larva to breathe. Extraction of the fly larva can be difficult, especially of the bot fly; extraction may be facilitated by first asphyxiating the larva, usually with an occlusive dressing or covering such as a bottle cap filled with petroleum jelly for several hours and then squeezing the larva out.
Tungiasis is caused by a sand flea Tunga penetrans. The female burrows into the skin, usually the foot, and produces a nodular, pale, subcutaneous lesion with a central dark spot.
The painful or pruritic lesion expands as the female produces eggs in her uterus. Loa loa filariasis occurs rarely in long-term travelers living in rural sub-Saharan Africa.
Navigation menu
The traveler may present with transient, migratory, subcutaneous, painful, or pruritic swellings produced by the adult nematode migration Calabar swelling. Rarely, the worm can be visualized crossing the conjunctiva of the eye or eyelid. Loiasis can be diagnosed by finding microfilariae in blood collected during daytime; however, since microfilaremia may be absent, filarial serologic tests may be helpful.
Gnathostomiasis is a nematode infection found primarily in Southeast Asia and less commonly in Africa and Latin America. Infection results from eating undercooked or raw freshwater fish. Infected travelers may experience transient, migratory, subcutaneous, pruritic, or painful swellings that may occur weeks or even years after exposure.
- Die großen Literaten der Welt: Amerika und Asien (marixwissen) (German Edition).
- The Labours of Love;
- The Celtic Languages (Routledge Language Family Series).
- Start Here;
The symptoms are due to migration of the worm through the body, and the central nervous system may be involved. Eosinophilia is common, and a definitive diagnosis is often difficult. Dermatologic conditions of the ill returned traveler: Int J Infect Dis. Macular lesions are common and often nonspecific and may be due to drug reactions or viral exanthems.
Superficial mycoses, such as tinea versicolor and tinea corporis, may also present as macular lesions. Tinea versicolor , due to Malassezia furfur previously Pityrosporum ovale , is characterized by asymptomatic hypopigmented or hyperpigmented oval, slightly scaly patches measuring 1—3 cm that are found on the upper chest, neck, and back. Treatment with topical or systemic azoles ketoconazole, fluconazole , terbinafine, or selenium sulfide present in some shampoos is recommended.
Tinea corporis ringworm may be caused by a number of different superficial fungi. The lesion is often a single lesion with an expanding red, raised ring, with a central area of clearing in the middle. The patient may not have noticed the tick bite. Leprosy Hansen disease frequently presents with hypopigmented or erythematous patches that are frequently hypoesthetic to pin prick and associated with peripheral nerve enlargement.
This condition is almost exclusively found in immigrants from developing countries. Cutaneous larva migrans , a skin infection with the larval stage of dog or cat hookworm Ancylostoma spp. A similar lesion that may be more urticarial and that rapidly progresses may be due to larva currens running larva due to cutaneous migration of filariform larvae of Strongyloides stercoralis. Lymphocutaneous spread of infection occurs when organisms spread along superficial cutaneous lymphatics, producing raised, linear, cord-like lesions; nodules or ulcers may also be found.
Examples include sporotrichosis, Mycobacterium marinum infection associated with exposure to water , leishmaniasis, bartonellosis cat-scratch disease , Nocardia infection, tularemia, melioidosis, and blastomycosis.
Skin & Soft Tissue Infections in Returned Travelers
Necrotizing fasciitis is a type of soft tissue infection. It can destroy the tissue in your skin and muscles as well as subcutaneous tissue, which is…. Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection. Cellulitis may first appear as a red, swollen area that feels hot and tender to the touch.
Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. This condition is contagious and can spread to the…. Infected eczema is common in people who have frequent eczema outbreaks. However, not all people with eczema will experience infections. Many people have experienced an occasional skin rash or unexplained mark.
Some conditions that cause skin rashes are very contagious. There are many different skin disorders. Some skin disorders, like contact dermatitis, are temporary and relatively minor, while others, like…. Tattoo infections aren't likely if you take care of the area after you get inked. Here's how to identify and treat an…. What are the types of skin infections? Pictures of types of skin infections. What are the symptoms of a skin infection? What are causes and risk factors for a skin infection? How is a skin infection diagnosed? How is a skin infection treated? Outlook for a skin infection.
Skin diseases: List of common conditions and symptoms
Candidiasis of the Skin Cutaneous Candidiasis. Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment. Necrotizing Fasciitis Soft Tissue Inflammation. Scabies Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a tiny, burrowing bug. Candidiasis of the Skin Cutaneous Candidiasis Candidiasis of the skin is a fungal infection that causes a red, itchy rash. Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment We explain the basics of impetigo, a highly contagious bacterial infection of the skin.
Necrotizing Fasciitis Soft Tissue Inflammation Necrotizing fasciitis is a type of soft tissue infection.