- Susannahs Saviors [Becketts Wolf Pack, Triad Mates 3] (Siren Publishing Menage & More).
- Unmanned combat aerial vehicle.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (Renal Disease) Avoid Dialysis, Get Your Life Back & Build Your Own Kidney Diet Plan; Regain Your Energy, Your Health and Save Your Life!;
- Main navigation.
While their counterparts in France were locked in stalemate during World War I , British troops protecting oil resources in the Persian Gulf were anything but. They pushed north against the Ottoman Empire, taking Baghdad in They routed the Ottomans at Mosul in October The news of their adventures boosted British morale. After the war ended on Nov.
They were unwilling to relinquish a region that had become crucial to imperial land and air routes, and whose potential wealth offered redemption from the losses of the war. Iraqis rebelled in , while Britain also faced rebellion in India, Ireland, Egypt and elsewhere. Using the deadly new Royal Air Force, Britain crushed the rebellion in a year. In this they built on wartime use of airpower in Iraq.
Subscribe to read | Financial Times
Thus it was that aerial photography and signaling were developed in wartime Iraq. Aircraft also supported the uniquely innovative deception and irregular warfare tactics the British used in the Middle East, which inspired the tactics of World War II. It was in the Middle East that the British invented the aerial trap — bombarding an Ottoman column retreating through a canyon — and the airlift. Postwar Cabinet assessments concluded that airpower had found greatest application in the Middle Eastern theaters of the war; it was there that it had proved its independent military capabilities.
After the rebellion, with the British public clamoring for demobilization, British officials again turned to airpower, now as a means for ruling Iraq. The RAF would patrol the country, coordinating information from agents on the ground to bomb villages and tribes.
History of unmanned aerial vehicles
But their most well-known and controversial use is by the military for reconnaissance, surveillance and targeted attacks. They are mostly used for surveillance in areas and terrains where troops are unable to safely go.
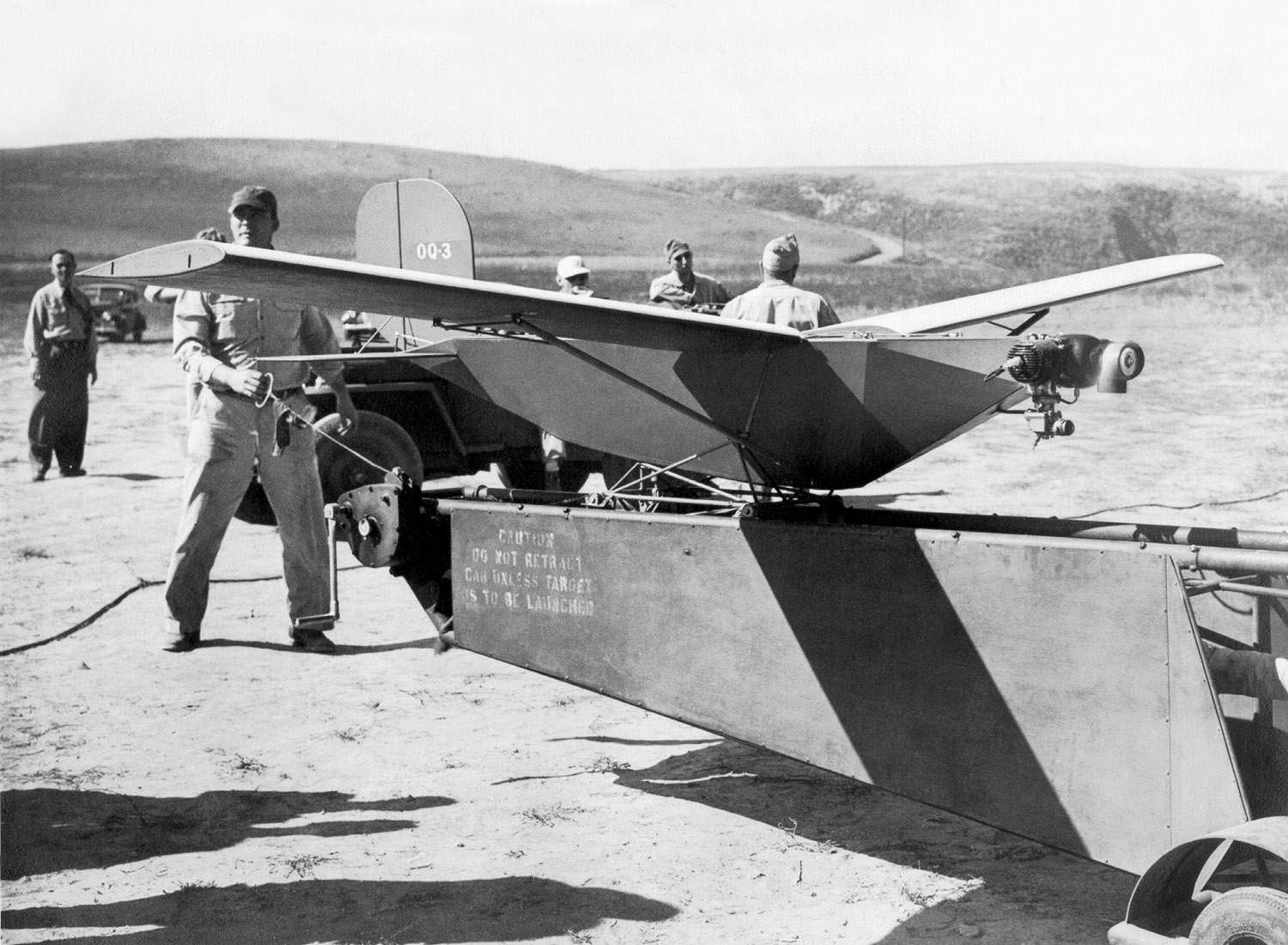
But they are also used as weapons and have been credited with killing suspected militants. The Queen Bee pilotless target drone was a radio-controlled version of the Tiger Moth trainer.
What we do
This 2,mile journey involved two of these prototypes, taking almost 15 hours and setting a new endurance record for remote controlled aircraft. This was the first of a family of new drones acquired by the Royal Artillery in the s to extend observation over the battlefield and to locate targets for new long range weapons.
- What is a Drone? - Unmanned Aircraft Technology Explained?
- Unmanned aerial vehicle - Wikipedia;
- History of unmanned aerial vehicles - Wikipedia.
- The Radio Rebel Trivia Book.
- How the Predator Drone Changed the Character of War | History | Smithsonian.
The men, kneeling several yards away from the vehicle, control the drone through a remote keypad and joystick. The rocket powered Midge Drone was designed to carry out aerial photo reconnaissance on a pre-programmed flight.
Accessibility Navigation
It was equipped with a single camera loaded with either black and white photographic film daylight missions or infra-red night missions. A pilotless drone aircraft designed for reconnaissance and artillery spotting used by British forces in the Gulf War , The interior of a pod at RAF Waddington from where the pilot left and sensor operator right fly an MQ-9 Reaper unpiloted aircraft on missions as part of Operation Shader. The Reaper is used for surveillance and reconnaissance, but is also armed for airstrikes.
Tuesday 30 January Here are 10 photographs of drones. The First World War saw the use of air power in conflict on a large scale for the first time.